Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC), a modified cellulose ether, has become a cornerstone in the construction industry due to its exceptional properties such as water retention, adhesion, and workability. This article provides an in-depth exploration of HPMC's technical specifications, applications, and the company behind this innovative product, Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd.. Through a detailed analysis of its chemical characteristics, practical uses, and industry relevance, we highlight why HPMC is a critical component in modern construction materials.



Understanding Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC)
HPMC is a semi-synthetic polymer derived from cellulose, a natural polysaccharide found in plant cell walls. Through a chemical process called etherification, hydroxypropyl and methyl groups are introduced to the cellulose backbone, enhancing its solubility, stability, and functional properties. This modification makes HPMC an ideal additive for construction materials, where it serves as a thickener, water retention agent, and film-forming agent.
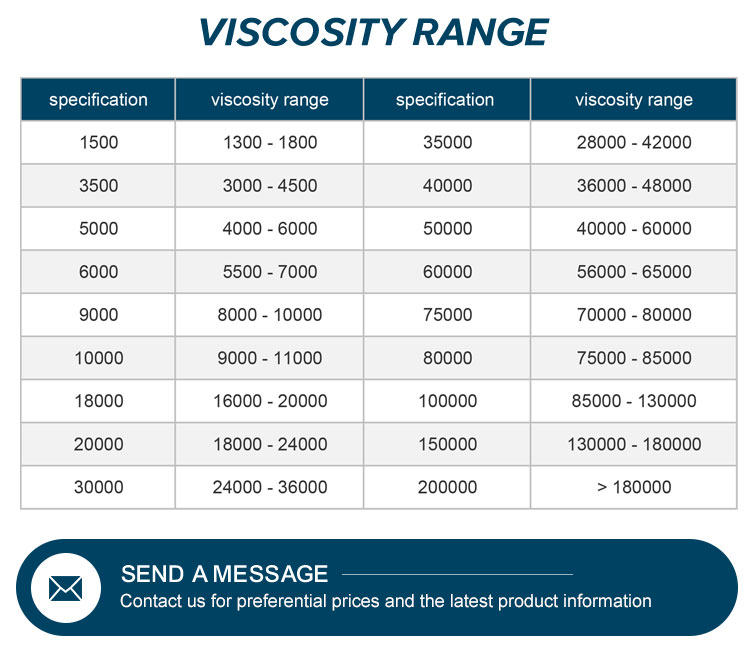
As a key chemical auxiliary agent, HPMC is also known as methyl hydroxy ether cellulose (MHEC). Its CAS number is 9004-65-3, and it is available in a pure form with a 99% purity rating. The product is typically packaged in 25 kg net weight units, making it convenient for industrial use.
Key Technical Specifications of HPMC
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Milky white or white powder |
| Carbonization Temperature | 280-300°C |
| Color Temperature | 190-200°C |
| Particle Size | 100 mesh pass rate >98.8%, 80 mesh pass rate 99.9%, special specifications 40-60 mesh |
| Apparent Density | 0.25-0.70 g/cm³ (typically 0.5 g/cm³) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.26-1.31 |
| Solubility | Soluble in water and certain solvents (e.g., ethanol/water, propanol/water) |
Core Advantages of HPMC in Construction
HPMC's unique chemical structure grants it several properties that make it indispensable in construction applications:
- Water Retention: HPMC improves the water retention of cement mortars and plasters, preventing rapid drying and ensuring optimal hydration of cementitious materials.
- Adhesion and Cohesion: It enhances the adhesion of tile adhesives and coatings to substrates, reducing the risk of delamination or cracking.
- Workability: By increasing the viscosity of cementitious mixtures, HPMC improves the workability of mortars and grouts, making them easier to apply.
- Dimensional Stability: HPMC minimizes shrinkage and cracking in dried materials, ensuring long-term structural integrity.
- Mildew Resistance: Its biocidal properties inhibit mold and bacterial growth, extending the lifespan of construction materials.
These advantages are further supported by NIST (National Institute of Standards and Technology) research on polymer-based additives, which emphasizes the role of hydrophilic polymers in improving material performance. NIST's work on nanomaterials and construction standards underscores the importance of additives like HPMC in modern infrastructure.
Applications in the Construction Industry
HPMC is widely used across various construction sectors, including:
1. Cement Mortar
HPMC is added to cement mortars to enhance their workability and water retention. This ensures even distribution of the mixture and reduces the likelihood of cracks during curing. According to NIST's guidelines on cementitious materials, such additives are critical for achieving high-performance concrete.
2. Ceramic Tile Adhesive
In tile installation, HPMC improves the bonding strength between tiles and substrates. Its water retention properties prevent the adhesive from drying too quickly, allowing for better alignment and placement of tiles. This is particularly important in large-scale projects where precision is essential.
3. Refractory Coatings
HPMC acts as a suspension agent and fluidity improver in asbestos and refractory coatings. It enhances the adhesion of these materials to high-temperature surfaces, making them suitable for industrial applications.
4. Gypsum Coagulant Slurry
When used in gypsum-based products, HPMC improves water retention and adhesion, ensuring a smooth and durable finish. This is crucial for applications like drywall and plasterboard.
5. Joint Cement
HPMC is added to joint cement for gypsum boards to improve fluidity and water retention. This ensures a strong bond between panels, reducing the risk of structural failures.








About Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd.
Based in Shijiazhuang, Hebei Province, China, Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd. is a leading manufacturer of cellulose-based chemical additives. With over a decade of expertise in the industry, the company specializes in producing high-quality HPMC for construction, pharmaceutical, and industrial applications.
The company's commitment to innovation and quality is reflected in its rigorous production processes and adherence to international standards. By leveraging advanced technologies and sustainable practices, Yongfeng Cellulose ensures that its products meet the demands of a rapidly evolving market.
For more information about the company's products and services, visit www.youngcel.com.
Conclusion
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) is a vital component in modern construction, offering a unique combination of properties that enhance the performance of cementitious and coating materials. Its ability to improve workability, adhesion, and durability makes it an indispensable additive in the industry. As highlighted by NIST's research on polymer-based materials, HPMC represents a significant advancement in construction technology.
Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd. continues to lead the way in providing high-quality HPMC solutions, ensuring that construction professionals have access to reliable and effective products. Whether used in tile adhesives, refractory coatings, or gypsum-based materials, HPMC remains a cornerstone of innovation in the construction sector.
References
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) (2025). Research on Polymer-Based Additives in Construction Materials. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov.
-
Understanding Methyl 2 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose: Uses, Benefits & Industry InsightsNewsNov.24,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose HEMC: Industrial Uses, Benefits & Future TrendsNewsNov.23,2025
-
HEMC Cellulose: Versatile & Sustainable Industrial Polymer | YoungcelNewsNov.23,2025
-
Methyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose: Versatile Building Block for Industry & SustainabilityNewsNov.23,2025
-
CAS 9032 42 2: Understanding Polyvinyl Alcohol's Impact on Industry & SustainabilityNewsNov.22,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose: Versatile Solutions for Modern Industry and SustainabilityNewsNov.22,2025




