
Introduction
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) is a versatile chemical additive widely used in the construction industry. As a modified cellulose ether, HPMC offers exceptional properties such as water retention, film-forming ability, and stability, making it an essential component in tile adhesives, cement mortars, and plaster additives. This article provides a comprehensive overview of HPMC's technical specifications, applications, and the company behind its production, Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd..
Product Overview
HPMC is derived from high-purity cotton fibers through a specialized etherification process under alkaline conditions. The resulting product is a white or milky white powder with a unique combination of physical and chemical properties. Its molecular structure allows it to dissolve in water and certain solvents, forming clear, stable solutions with surface activity. This makes HPMC ideal for applications requiring improved workability, adhesion, and durability.


Key Characteristics
- Thickening Ability: Enhances the viscosity of cementitious materials without compromising workability.
- Salt Resistance: Maintains performance in the presence of salts, common in construction environments.
- Water Retention: Prevents premature drying of mortars and adhesives, ensuring proper curing.
- Dimensional Stability: Reduces shrinkage and cracking in finished products.
- Adhesion and Dispersibility: Improves bonding strength and uniformity in mixtures.
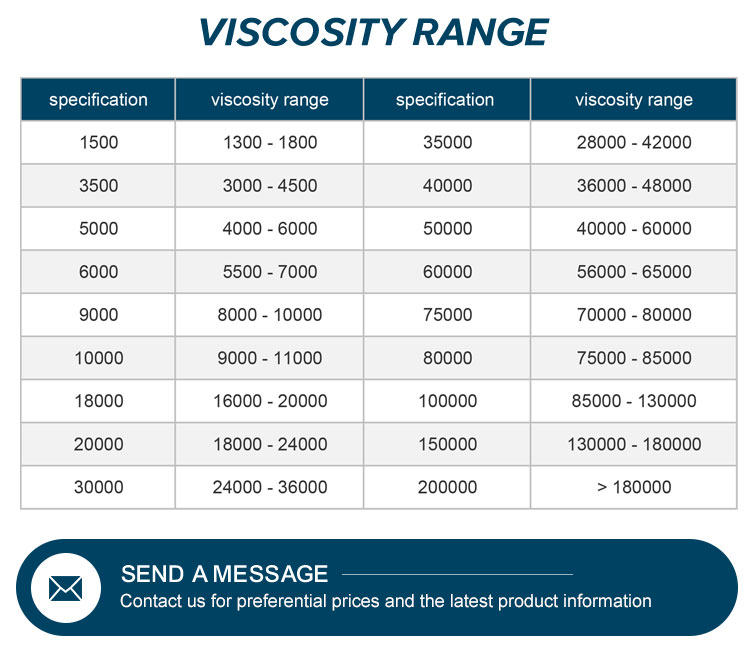
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Milky white or white powder |
| Carbonization Temperature | 280-300°C |
| Color Temperature | 190-200°C |
| Particle Size | 100 mesh: >98.8%; 80 mesh: 99.9%; 40-60 mesh (special) |
| Apparent Density | 0.25-0.70 g/cm³ (typically 0.5 g/cm³) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.26-1.31 |
| Solubility | Water and solvents (e.g., ethanol/water, propanol/water) |

Applications in the Construction Industry
HPMC's versatility makes it suitable for a wide range of construction applications:
1. Cement Mortar
HPMC improves the workability and water retention of cement mortars, ensuring even application and reducing cracking. It enhances the adhesion between the mortar and the substrate, making it ideal for both interior and exterior use.
2. Ceramic Tile Cement
In ceramic tile adhesives, HPMC provides excellent bonding strength and flexibility. Its water retention properties prevent the cement from drying too quickly, allowing for proper tile alignment and long-term durability.
3. Refractory Coatings
HPMC acts as a suspension agent and fluidity improver in asbestos and refractory coatings. It enhances the adhesion of these materials to substrates, improving their thermal resistance and structural integrity.
4. Gypsum Coagulant Slurry
When added to gypsum slurry, HPMC improves water retention and workability, ensuring a smooth finish and strong adhesion to the substrate. This is critical for applications like drywall and plasterboard.
5. Joint Cement
HPMC is used in joint cement for gypsum boards to improve fluidity and water retention. This results in stronger, more flexible joints that resist cracking over time.


Company Background: Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd.
Based in Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd., the manufacturer of HPMC, is a leading producer of cellulose derivatives. With years of expertise in the chemical industry, the company specializes in the development and production of high-quality additives for construction and industrial applications. Their commitment to innovation and quality control ensures that their products meet international standards.


Industry Standards and Research
The performance and reliability of HPMC are supported by rigorous testing and adherence to industry standards. According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), the development of advanced materials like HPMC requires precise measurements and standardized protocols to ensure consistency and safety. NIST's research on polymer-based additives highlights the importance of properties such as water retention and dimensional stability in construction materials (NIST, 2023).

Conclusion
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) is a critical additive in modern construction, offering unmatched performance in tile adhesives, mortars, and plaster products. Its unique properties, combined with the expertise of Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd., make it a trusted solution for professionals worldwide. As the construction industry continues to evolve, HPMC remains a cornerstone of innovation, supported by rigorous standards and research, including contributions from institutions like NIST.
References
NIST. (2023). Advanced Materials Research. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/
-
Understanding Methyl 2 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose: Uses, Benefits & Industry InsightsNewsNov.24,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose HEMC: Industrial Uses, Benefits & Future TrendsNewsNov.23,2025
-
HEMC Cellulose: Versatile & Sustainable Industrial Polymer | YoungcelNewsNov.23,2025
-
Methyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose: Versatile Building Block for Industry & SustainabilityNewsNov.23,2025
-
CAS 9032 42 2: Understanding Polyvinyl Alcohol's Impact on Industry & SustainabilityNewsNov.22,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose: Versatile Solutions for Modern Industry and SustainabilityNewsNov.22,2025




