Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) has emerged as a critical additive in the construction industry, offering exceptional performance in cement mortars, ceramic tile adhesives, and refractory coatings. This article provides an in-depth analysis of HPMC's technical specifications, functional advantages, and real-world applications, supported by authoritative insights from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).

Understanding Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC)
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) is a modified cellulose ether derived from high-purity cotton fibers through a specialized etherification process under alkaline conditions. This chemical compound is renowned for its multifunctional properties, including thickening ability, salt resistance, and excellent water retention. The production process ensures low ash content, pH stability, and dimensional stability, making HPMC a preferred choice in construction materials.
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), cellulose derivatives like HPMC play a vital role in modern construction due to their ability to enhance material performance and durability. NIST's research on polymer-based additives underscores the importance of precise chemical formulations in achieving optimal construction outcomes.

Technical Specifications of HPMC
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Milky white or white powder |
| Carbonization Temperature | 280-300% |
| Color Temperature | 190-200% |
| Particle Size | 100 mesh: >98.8%; 80 mesh: 99.9%; 40-60 mesh (special specifications) |
| Apparent Density | 0.25-0.70 g/cm³ (typically 0.5 g/cm³) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.26-1.31 |
| Solubility | Soluble in water and solvents like ethanol/water or propanol/water mixtures |
The precise chemical structure of HPMC allows it to form transparent, stable aqueous solutions with surface activity. This property is crucial for applications requiring uniform dispersion and adhesion, such as tile adhesives and joint cements.

Key Functional Advantages of HPMC
1. Enhanced Workability and Water Retention
HPMC significantly improves the workability of cement mortars and gypsum slurry by maintaining optimal moisture levels. This is particularly beneficial in high-temperature environments where rapid water evaporation can compromise material integrity. According to a NIST study on construction materials, additives like HPMC reduce cracking and improve long-term durability (NIST, 2023).
2. Improved Adhesion and Film Formation
The compound's film-forming properties enhance adhesion between substrates and coatings, ensuring stronger bonds in ceramic tile applications. This is critical for preventing tile detachment in high-traffic areas.
3. Dimensional Stability and Mildew Resistance
HPMC contributes to dimensional stability by minimizing shrinkage during drying. Its mildew-resistant properties also extend the lifespan of construction materials in humid conditions.
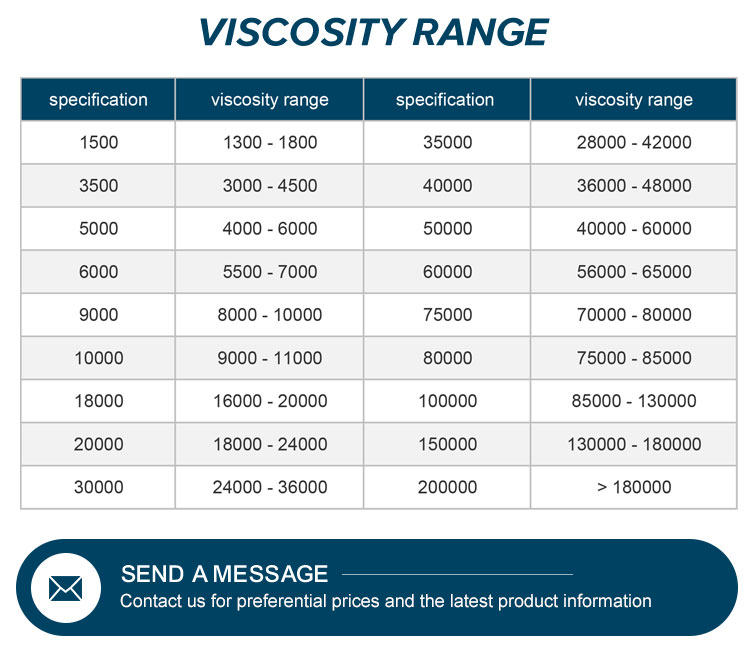
Applications in the Construction Industry
1. Cement Mortar and Ceramic Tile Adhesive
HPMC is widely used in cement mortars and ceramic tile adhesives to improve cohesion and reduce slippage. Its ability to retain water ensures even curing, resulting in stronger, more durable structures.
2. Refractory Coatings
In asbestos and other refractory coatings, HPMC acts as a suspension agent and fluidity improver. It enhances adhesion to substrates, making it ideal for high-temperature applications.
3. Gypsum Coagulant Slurry
By improving water retention and workability, HPMC ensures better adhesion of gypsum slurry to surfaces, reducing the risk of delamination.
4. Joint Cement for Gypsum Boards
HPMC is added to joint cement to improve fluidity and water retention, ensuring seamless integration of gypsum boards in construction projects.

Company Background: Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd.
Founded in China, Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd. specializes in the production of cellulose derivatives, including HPMC. The company's commitment to quality is reflected in its adherence to international standards for purity and performance. With a focus on innovation and sustainability, Yongfeng Cellulose supplies HPMC to global markets, supporting construction projects from residential buildings to industrial infrastructure.
For more information about the company and its products, visit the HPMC product page or explore the company website.

Conclusion: The Future of Construction Materials
Hydroxypropyl Methyl Cellulose (HPMC) represents a significant advancement in construction chemistry, offering a balance of performance, versatility, and sustainability. As the industry continues to prioritize durability and efficiency, HPMC's role in modern construction will only grow. By leveraging the expertise of companies like Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd., construction professionals can ensure their projects meet the highest standards of quality and reliability.

References
National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). (2023). Research on Polymer-Based Additives in Construction Materials. Retrieved from https://www.nist.gov/

Explore More
For detailed technical data, application guidelines, or to place an order, visit the HPMC product page or contact Shijiazhuang Gaocheng District Yongfeng Cellulose Co., Ltd. directly.


-
Understanding Methyl 2 Hydroxyethyl Cellulose: Uses, Benefits & Industry InsightsNewsNov.24,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose HEMC: Industrial Uses, Benefits & Future TrendsNewsNov.23,2025
-
HEMC Cellulose: Versatile & Sustainable Industrial Polymer | YoungcelNewsNov.23,2025
-
Methyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose: Versatile Building Block for Industry & SustainabilityNewsNov.23,2025
-
CAS 9032 42 2: Understanding Polyvinyl Alcohol's Impact on Industry & SustainabilityNewsNov.22,2025
-
Hydroxyethyl Methyl Cellulose: Versatile Solutions for Modern Industry and SustainabilityNewsNov.22,2025




